
Understanding genetic testing for Duchenne.
The latest genetic testing methods can identify specific mutations in the dystrophin gene. Identifying your child’s mutation will allow your doctor to determine amenability to VYONDYS 53. Patients with Duchenne who receive VYONDYS 53 must have a genetic test that shows a mutation in the dystrophin gene that can be treated by skipping exon 53.

Meet Luke, age 12
Amenable to exon 53 skipping
Getting familiar with genetic test reports.
After your child provides a blood or saliva sample, your doctor will send your child’s genetic sample to a lab to run the genetic test report. Each lab’s report looks a little different. Here are some of the key pieces of information you should be looking for as you read the genetic test report with your child’s doctor:

-
A Duchenne diagnosis.
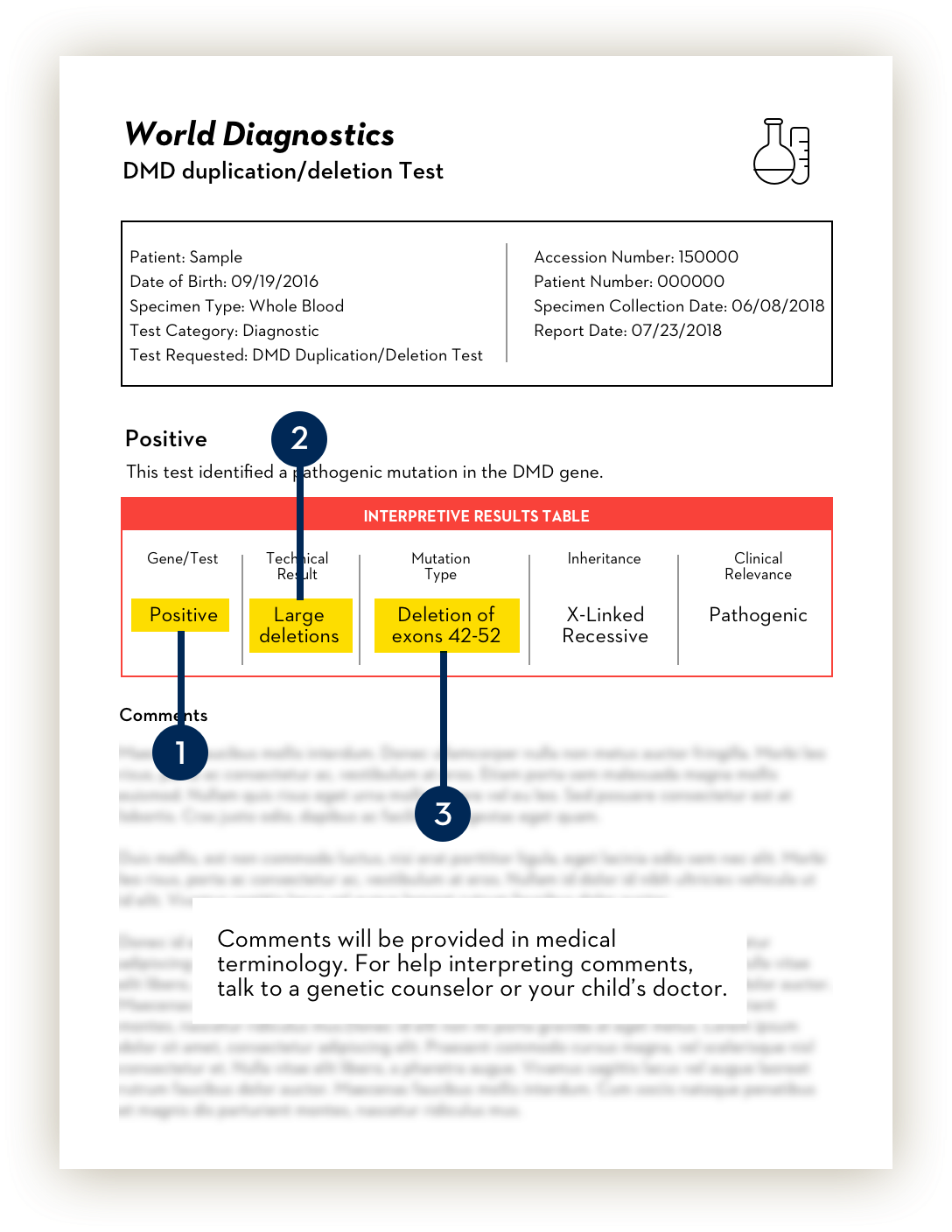
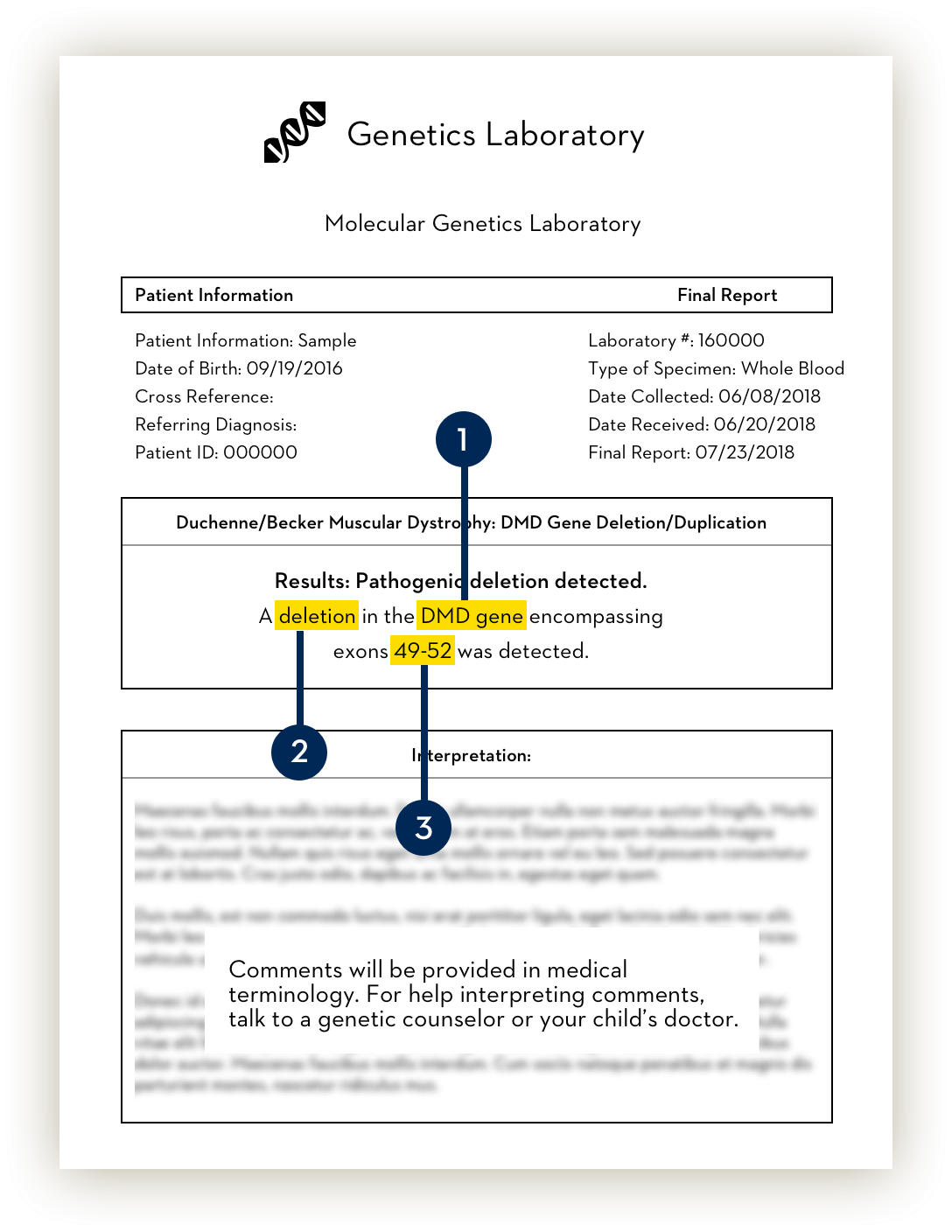
The genetic test report will identify if there are any mutations in the dystrophin, or DMD, gene that would confirm a Duchenne diagnosis.
What to look for: A confirmation that there is a mutation on the dystrophin, or DMD, gene. You might see terms like “Positive result,” “Mutation detected,” “Pathogenic variant detected,” or similar terms.
-
The type of mutation.
The test will provide information on the type of mutation in the dystrophin gene. There are three types of mutations:
- Large deletions: One or more exons are missing. This is the most common type and includes the ones targeted by VYONDYS 53.
- Large duplications: One or more exons are copied.
- Other changes: Small changes in the gene that do not include an entire exon.
What to look for: An indication that the type of mutation is a “deletion.”
-
The missing exons.
Your child’s doctor or genetic counselor will determine amenability to exon 53 skipping based on which exons are missing. If the genetic test report mentions deletions, it will also identify the “genomic region” or simply add a range of missing exons (e.g. 52).
What to look for: A number or number range stating which exons make up the deletion.

Discuss test results with your child's doctor or genetic counselor.
Whether your child has had a recent test, or you want to reexamine an older one, make sure to review the results with your child's doctor or genetic counselor as soon as possible to determine amenability to VYONDYS 53. In your conversation, you may want to ask:
- Did the test confirm Duchenne muscular dystrophy?
- What’s the type of genetic mutation?
- Does my child’s deletion show amenability to exon 53 skipping?
- Is VYONDYS 53 the right treatment option for us?
Explore our Doctor Discussion Guide.
It can be a challenge to remember all the information you want to when talking to your doctor. Utilize our helpful guide for information on what to ask during an appointment.
Related FAQs
Amenability describes the potential for your child to be treated with exon-skipping therapy. VYONDYS 53 is only for those whose Duchenne muscular dystrophy is the result of a genetic mutation amenable to exon 53 skipping. Find out more about genetic testing for Duchenne.
A mutation is a change in a person’s DNA. Mutations range in size from a small (a single rung on a ladder) to a large segment of DNA. Every mutation causes a different effect on our bodies. Learn more about the role of genetics in Duchenne.
Because Duchenne is a progressive disease, it’s important for your child’s doctor to confirm a diagnosis and identify the specific genetic mutation to guide your child’s care and treatment. More about the steps to diagnosis.
